硕士生导师
个人信息Personal Information
办公地点:犀浦校区X4537
主要任职:测绘遥感信息系副教授/硕士生导师
其他任职:中国测绘学会工程测量分会委员(2021-2026)/矿山与地下测量专委会委员(2018-2021,2022-2027)
所在单位:地球科学与工程学院
 报考该导师研究生的方式
报考该导师研究生的方式
欢迎你报考张同刚老师的研究生,报考有以下方式:
1、参加西南交通大学暑期夏令营活动,提交导师意向时,选择张同刚老师,你的所有申请信息将发送给张同刚老师,老师看到后将和你取得联系,点击此处参加夏令营活动
2、如果你能获得所在学校的推免生资格,欢迎通过推免方式申请张同刚老师研究生,可以通过系统的推免生预报名系统提交申请,并选择意向导师为张同刚老师,老师看到信息后将和你取得联系,点击此处推免生预报名
3、参加全国硕士研究生统一招生考试报考张同刚老师招收的专业和方向,进入复试后提交导师意向时选择张同刚老师。
4、如果你有兴趣攻读张同刚老师博士研究生,可以通过申请考核或者统一招考等方式报考该导师博士研究生。
学术论文
当前位置: Tonggang ZHANG >> 科学研究 >> 学术论文完整论文列表 成果应用 Baidu学术 ResearchGate SPIE Proceedings
面向轨道维护的可变轨距轨道模型与钢轨点云的配准方法
Registration Algorithm of Variable Gauge Track Model and Rail Point Cloud for Track Maintenance
陈丞, 张同刚, 李涛, 沈迅, 邓川, 金国清
铁道学报 2021 录用
Full Paper:
基于车载Lidar技术相关的硬件和算法的快速发展,具备发展成快速车载轨道测量技术手段的潜力,从而替代传统的地面人工轨道测量手段。本文针对其中根据钢轨点云获取轨道轨距、钢轨位置等参数的问题,定义了可变轨距轨道模型(VGT, Variable Gauge Track Model),并在此实现了可变轨距轨道模型与钢轨点云的配准方法。新算法在配准迭代过程根据钢轨点云到轨道工作边的距离来动态调整模型轨距,从而在轨道配准精度和轨距测量精度两项关键指标获得了同步提高。通过模拟数分析了存在不同轨距偏差、超高等情况下算法性能,并和单钢轨轨道模型和固定轨距轨道模型的配准结果进行了比较。最后通过一段干线铁路的实测点云进行测试,试验结果表明单钢轨轨道模型配准后左右钢轨的平行性得不到保证;在直线段与固定轨距轨道模型配准精度和轨距测量精度基本相当,配准精度为0.16mm;在曲线段可变轨距轨道模型配准精度和轨距测量精度不受轨距变化的影响,显著优于固定轨距轨道模型的结果。
Building contour extraction from Airborne Lidar point cloud for Digital Line Graphic
Yuhui KAN, Tonggang ZHANG*, Dan ZHONG, Shiqiang JIA, Fugui XIE
Proceedings of SPIE 11525, SPIE Future Sensing Technologies, 115250O (8 November 2020)
Full Paper: SPIE ResearchGate
Based on IMBR algorithm, this paper proposes an algorithm for building contour extraction which is suitable for different scale digital line graphic (DLG). The new algorithm solves the tooth contour that may occur when IMBR algorithm is used to extract building contour. Firstly, a plane extraction algorithm based on region growth is used to extract the point cloud of the building roof. The algorithm introduces graded seed points and neighborhood-constrained growth criteria to avoid dividing the tree point cloud into building planes. Then, a Foot Point Correction algorithm is proposed to avoid the tooth contour in IMBR algorithm. The experimental results show that the Correctness and completeness of extracting building roof point cloud are above 97%. There is no tooth contour in the extracted building contour, which can meet the requirements of generating DLG with different scales.
A rail extraction algorithm based on the generalized neighborhood height difference from mobile laser scanning data
Cheng CHEN, Tonggang ZHANG*,Yuhui KAN, Shichao LI, Guoqing JIN
Proceedings of SPIE 11525, SPIE Future Sensing Technologies, 115250N (8 November 2020)
Full Paper: SPIE ResearchGate
Accurate and complete rail extraction from mobile laser scanning (MLS) data is currently a fundamental and challenging problem for its application on the railway. By using the track knowledge, a signed cylindrical neighborhood difference is defined as the rail descriptor and then proposed a new rail extraction algorithm from MLS data. It can extract accurate, continuous, and complete railhead, which is most critical for the rail geometric parameter and centerline, of the entire railway. Moreover, it can successfully extract the railhead of the main-line, including the curve section with different superelevation, and turnout. A 3-km long trunk railway, including main-line and turnout, straight line and curve line, located in the southwest of China is selected to test the performance of the proposed rail extraction algorithm. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can correctly extract the railhead of the whole railway, with an overall accuracy (F-measure) of 88.73%. Its accuracy is improved by 42.68% compared with the rail extraction algorithm based on spherical neighborhood difference.
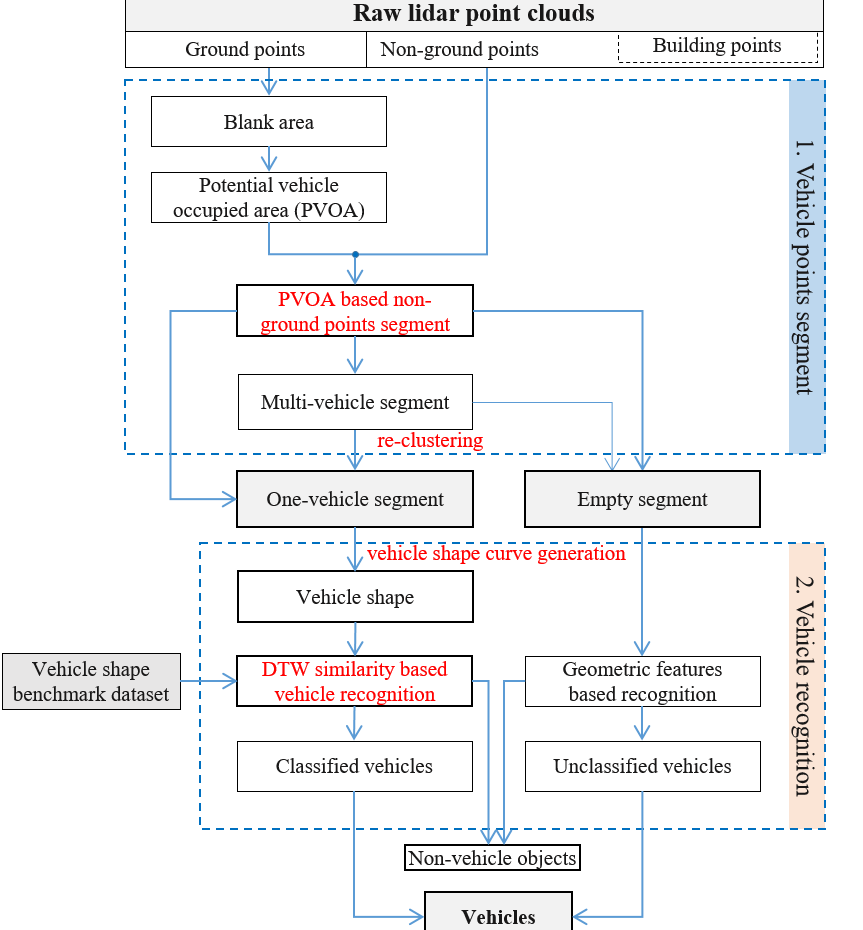
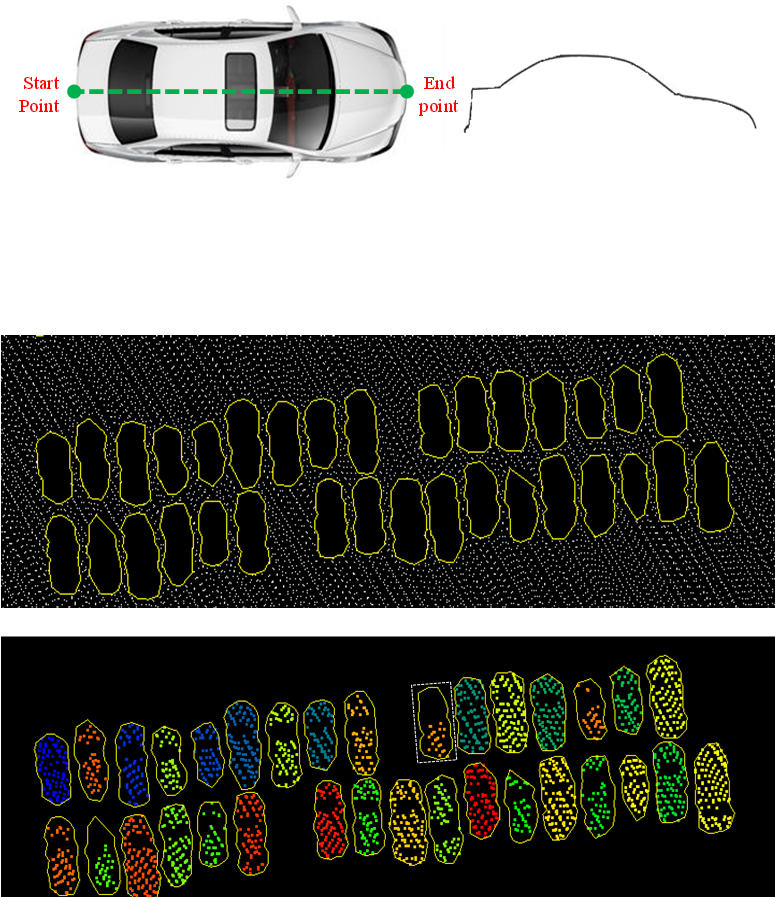
Urban Vehicle Extraction from Aerial Laser Scanning Point Cloud Data
Tonggang ZHANG*, Yuhui KAN, Hailong JIA, Chuan DENG, Tingsong XING
International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 41(17), 6664–6697
Full Paper: IJRS ResearchGate
A vehicle extraction method is proposed in this paper to extract vehicles in urban areas more accurately from airborne point clouds. First, the ground points are separated from the non-ground points, and a potential vehicle-occupied area (PVOA) is then extracted from the ground point cloud. A PVOA-based non-ground point cloud segmentation method is proposed in this work, and a gap-based method is put forward to re-cluster the segment, which may include multiple vehicles. The non-ground point cloud is clustered into a series of one-vehicle segments and empty segments. Following this, a shape-based vehicle recognition method is presented that can judge whether or not a given segment is a vehicle using a dynamic time warping similarity measurement. In addition to judging whether or not a segment is a vehicle, the category of each vehicle can also be determined...
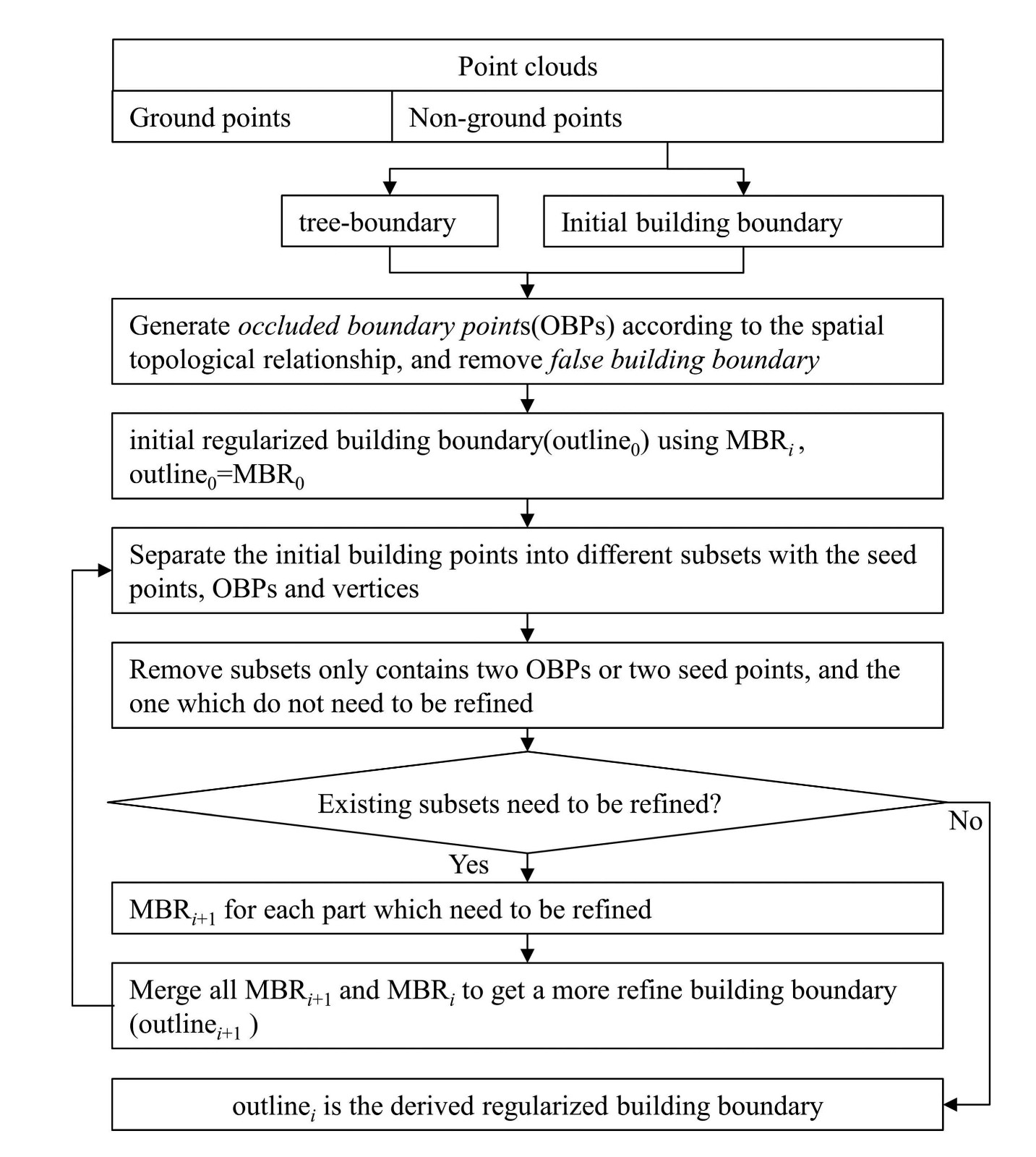
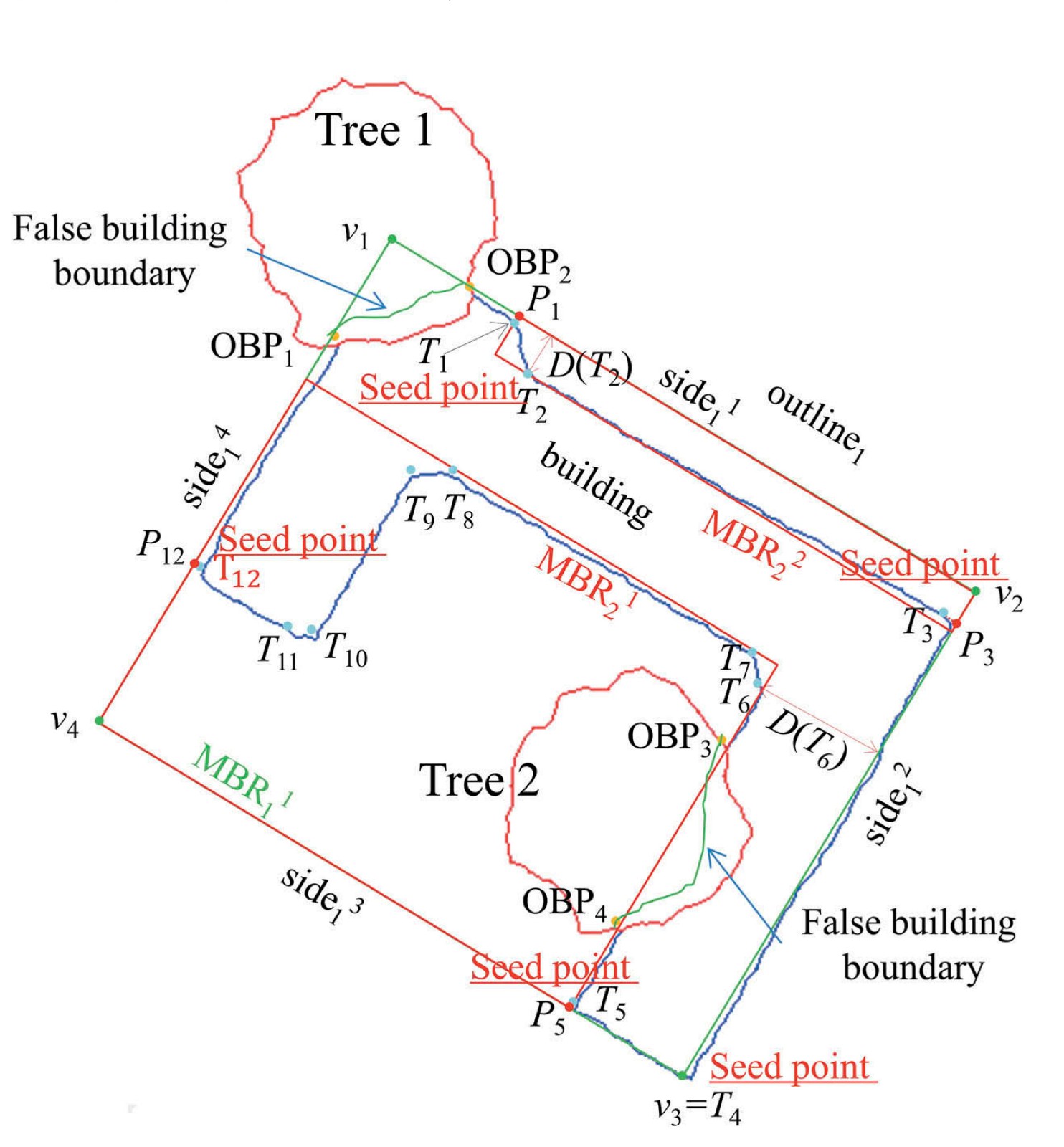
An improved minimum bounding rectangle algorithm for regularized building boundary extraction from aerial LiDAR point clouds with partial occlusions
Maolin FENG, Tonggang ZHANG(*), Shichao LI, Guoqing JIN, Yanjun XIA
International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 41(1), 200-219
Full Paper: ResearchGate IJRS
In this paper, we propose an improved minimum bounding rectangle (IMBR) algorithm to extract complete and accurate regularized building boundaries with and without partial occlusion from aerial LiDAR point clouds. The new algorithm only uses LiDAR point cloud and doesn't need any additional data source. In addition, the algorithm can be applied to buildings with complex shapes....